-
 Prof. Li's group discovered a novel mechanism and drug target of Type 2 diabetes
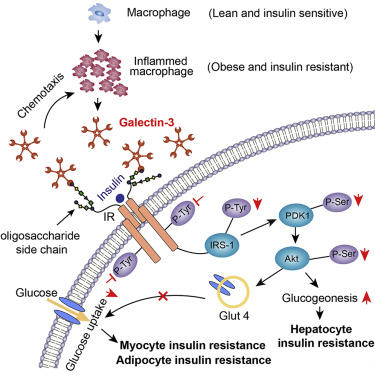
Insulin resistance is the hallmarker of Type 2 diabetes and accumulating evidence show that inflammation plays a key role in obesity associated insulin resistance. Recently, Cell published the latest finding in Prof. Li Pingping's lab about inflammatory factor Galectin-3 (Gal3),Which is mainly secreted by macrophages. Prof. Li's group showed that Gal3 can directly bind to the insulin receptor and impair insulin signaling pathway in hepatocyte, adipocyte, and myocyte, then lead to the insulin res...
2016-12-12
Prof. Li's group discovered a novel mechanism and drug target of Type 2 diabetes
Insulin resistance is the hallmarker of Type 2 diabetes and accumulating evidence show that inflammation plays a key role in obesity associated insulin resistance. Recently, Cell published the latest finding in Prof. Li Pingping's lab about inflammatory factor Galectin-3 (Gal3),Which is mainly secreted by macrophages. Prof. Li's group showed that Gal3 can directly bind to the insulin receptor and impair insulin signaling pathway in hepatocyte, adipocyte, and myocyte, then lead to the insulin res...
2016-12-12
-
 A novel hypoxia-responsive siRNA delivery system for tumor-targeted therapy developed by Prof. Gao Zhonggao’s group
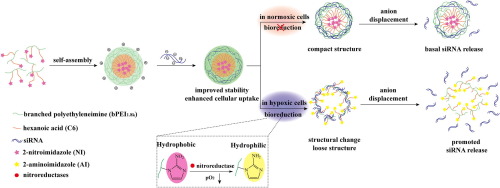
Most solid tumors contain a tumor-specific microenvironment that is characterized by low pO2 , also known as hypoxia. Owing to the rapid proliferation of cancer cells, the tumor quickly exhausts the nutrient and oxygen supplied from the vasculature, and becomes hypoxic. Targeting hypoxia is considered as the best validated yet not extensively exploited strategy in cancer therapy. Recently, a research article entitled "an effective tumor-targeting strategy utilizing hypoxia-sensitive siRNA delive...
2016-10-21
A novel hypoxia-responsive siRNA delivery system for tumor-targeted therapy developed by Prof. Gao Zhonggao’s group
Most solid tumors contain a tumor-specific microenvironment that is characterized by low pO2 , also known as hypoxia. Owing to the rapid proliferation of cancer cells, the tumor quickly exhausts the nutrient and oxygen supplied from the vasculature, and becomes hypoxic. Targeting hypoxia is considered as the best validated yet not extensively exploited strategy in cancer therapy. Recently, a research article entitled "an effective tumor-targeting strategy utilizing hypoxia-sensitive siRNA delive...
2016-10-21
-
 TRB3, a metabolic stresses sensor acts as a biologic link between diabetes and cancer
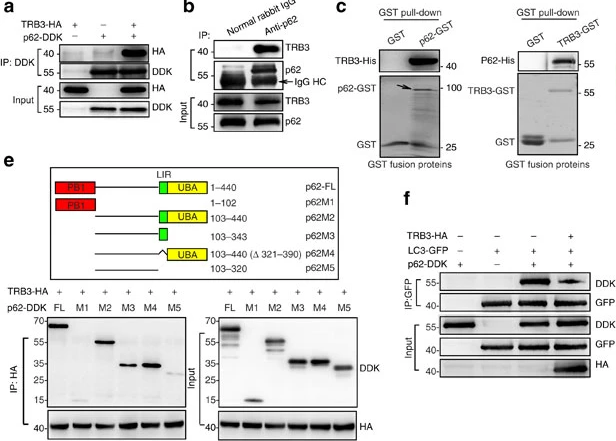
Type 2 diabetes is a serious and growing health problem worldwide. Clinical and epidemiologic studies have shown that diabetes carries an increased risk for different forms of cancer, but with undefined mechanisms. High insulin and IGF-1 in circulation have been considered to be the most potential biologic links between the two diseases. However, clinical trials show that targeting insulin/IGF-1 signal does not produce satisfactory efficacy against cancers. Prof. Zhuo-Wei Hu's group in State Key...
2015-08-22
TRB3, a metabolic stresses sensor acts as a biologic link between diabetes and cancer
Type 2 diabetes is a serious and growing health problem worldwide. Clinical and epidemiologic studies have shown that diabetes carries an increased risk for different forms of cancer, but with undefined mechanisms. High insulin and IGF-1 in circulation have been considered to be the most potential biologic links between the two diseases. However, clinical trials show that targeting insulin/IGF-1 signal does not produce satisfactory efficacy against cancers. Prof. Zhuo-Wei Hu's group in State Key...
2015-08-22
-
 A novel advancement on targeting delivery of anticancer agents in Prof. Gao Zhonggao’s group
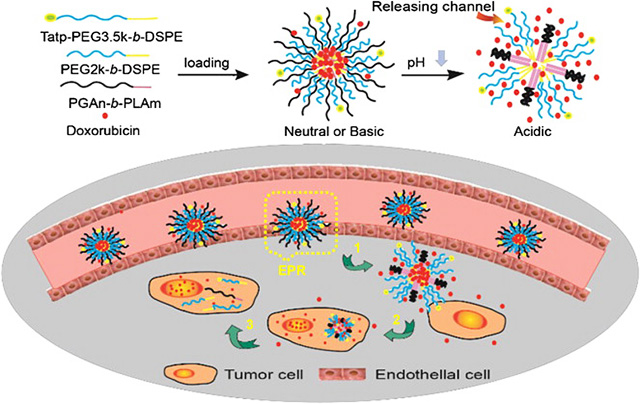
Recently, Prof. Gao Zhonggao's group, in the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, have published an original research paper entitled "Hybrid polymeric micelles based on bioactive polypeptides as pH-responsive delivery systems against melanoma" on Biomaterials (the impact factor was 7.604 published in 2013, with the 5-year impact factor of 8.496), an top international journal in the field of biomaterials and pharmaceutics. Now, the article is available o...
2014-07-07
A novel advancement on targeting delivery of anticancer agents in Prof. Gao Zhonggao’s group
Recently, Prof. Gao Zhonggao's group, in the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, have published an original research paper entitled "Hybrid polymeric micelles based on bioactive polypeptides as pH-responsive delivery systems against melanoma" on Biomaterials (the impact factor was 7.604 published in 2013, with the 5-year impact factor of 8.496), an top international journal in the field of biomaterials and pharmaceutics. Now, the article is available o...
2014-07-07
-
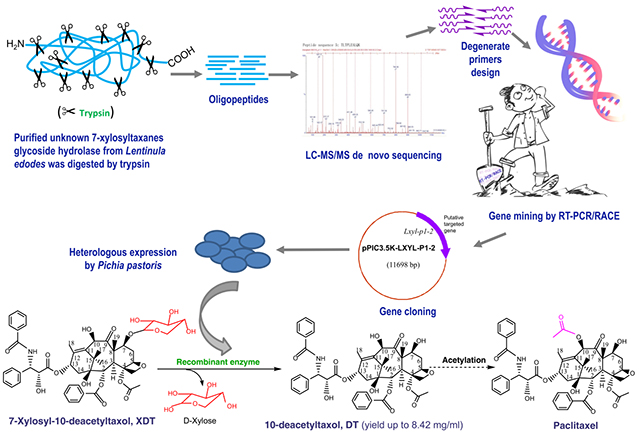 Professor Zhu Ping's group published paper on Molecular & Cellular Proteomics
On May 10, 2013, Professor Zhu's group of the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines published (online) the article: Cloning and characterization of the glycoside hydrolases that remove xylosyl group from 7-β-xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol and its analogues (doi:10.1074/mcp.M113.030619) on Molecular & Cellular Proteomics (MCP), an international top journal in the field of proteomics (http://www.mcponline.org/content/early/recent) (the impact factor was 7.398 publ...
2013-05-29
Professor Zhu Ping's group published paper on Molecular & Cellular Proteomics
On May 10, 2013, Professor Zhu's group of the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines published (online) the article: Cloning and characterization of the glycoside hydrolases that remove xylosyl group from 7-β-xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol and its analogues (doi:10.1074/mcp.M113.030619) on Molecular & Cellular Proteomics (MCP), an international top journal in the field of proteomics (http://www.mcponline.org/content/early/recent) (the impact factor was 7.398 publ...
2013-05-29
-
 New advancement on siRNA drug delivery in Prof. Gao Zhonggao's group
Recently, a research article entitled "Anti-tumor effects in mice induced by survivin-targeted siRNA delivered through polysaccharide nanoparticles" in Prof. Gao Zhonggao' group in the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines has been published by the international authorized journal "Biomaterials" in the fields of biomaterials and pharmaceutics. Currently, this article is available online (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.03.047).
By inducing R...
2013-05-22
New advancement on siRNA drug delivery in Prof. Gao Zhonggao's group
Recently, a research article entitled "Anti-tumor effects in mice induced by survivin-targeted siRNA delivered through polysaccharide nanoparticles" in Prof. Gao Zhonggao' group in the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines has been published by the international authorized journal "Biomaterials" in the fields of biomaterials and pharmaceutics. Currently, this article is available online (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.03.047).
By inducing R...
2013-05-22
-
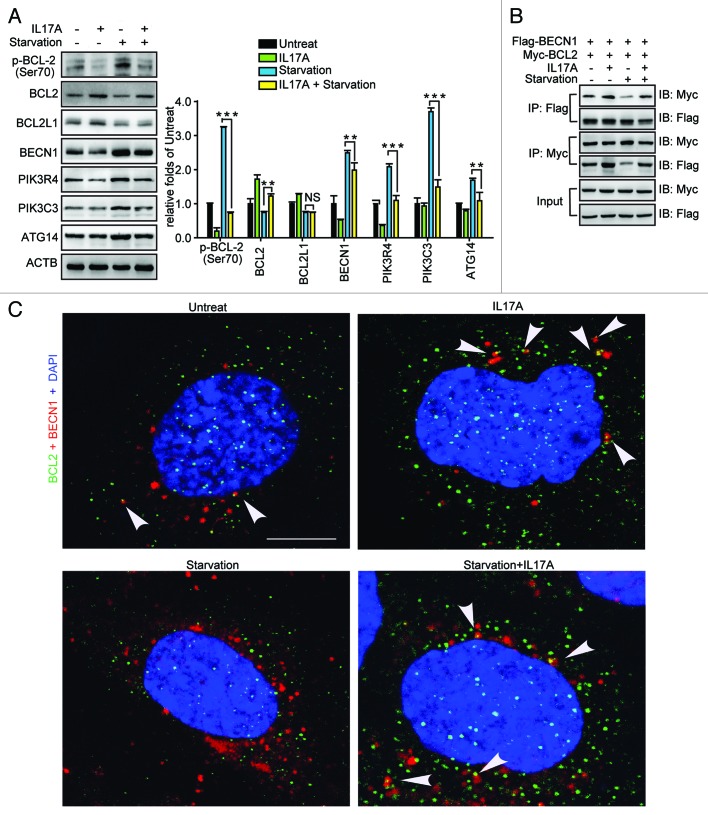 Dr. Zhuowei Hu group's work reveals the mechanism of IL17A suppressing autophagy
Dr. Zhuowei Hu and his group have recently published a paper entitled "Interlukin 17A inhibits autophagy through activation of PIK3CA to interrupt the GSK3B-mediated degradation of BCL2 in lung epithelial cells" in "Autophagy", an international reputation magazine. The research paper has been published online. In a previous work by this group, researchersreported that IL-17A promotes the development and progression of pulmonary fibrosis through TGFβ1-dependent and -independent mechanisms (Mi et ...
2013-02-28
Dr. Zhuowei Hu group's work reveals the mechanism of IL17A suppressing autophagy
Dr. Zhuowei Hu and his group have recently published a paper entitled "Interlukin 17A inhibits autophagy through activation of PIK3CA to interrupt the GSK3B-mediated degradation of BCL2 in lung epithelial cells" in "Autophagy", an international reputation magazine. The research paper has been published online. In a previous work by this group, researchersreported that IL-17A promotes the development and progression of pulmonary fibrosis through TGFβ1-dependent and -independent mechanisms (Mi et ...
2013-02-28
-
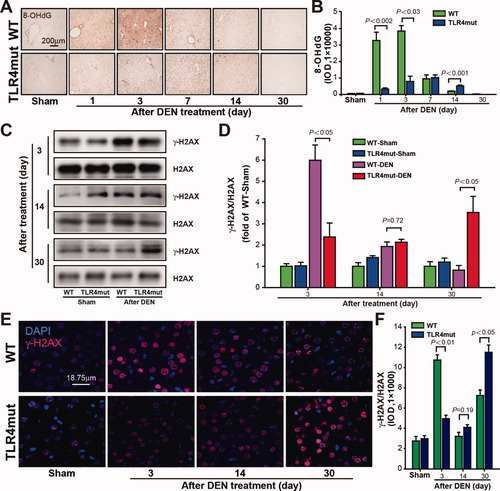 TLR4 activity protects against hepatocellular tumorigenesis and progression
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a devastating consequence of chronic inflammatory liver diseases. The underlying molecular mechanisms for the relationships between HCC and chronic inflammatory are needed to be completely elucidated. TLR4 exhibit different sides with regard to the roles in the regulation of carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Researchers discovered that genetic or pharmacology blocking of TLR4 increases susceptibility to DEN-induced HCC development. TLR4 mutation results in s...
2013-01-24
TLR4 activity protects against hepatocellular tumorigenesis and progression
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a devastating consequence of chronic inflammatory liver diseases. The underlying molecular mechanisms for the relationships between HCC and chronic inflammatory are needed to be completely elucidated. TLR4 exhibit different sides with regard to the roles in the regulation of carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Researchers discovered that genetic or pharmacology blocking of TLR4 increases susceptibility to DEN-induced HCC development. TLR4 mutation results in s...
2013-01-24
 Prof. Li's group discovered a novel mechanism and drug target of Type 2 diabetes
Insulin resistance is the hallmarker of Type 2 diabetes and accumulating evidence show that inflammation plays a key role in obesity associated insulin resistance. Recently, Cell published the latest finding in Prof. Li Pingping's lab about inflammatory factor Galectin-3 (Gal3),Which is mainly secreted by macrophages. Prof. Li's group showed that Gal3 can directly bind to the insulin receptor and impair insulin signaling pathway in hepatocyte, adipocyte, and myocyte, then lead to the insulin res...
2016-12-12
Prof. Li's group discovered a novel mechanism and drug target of Type 2 diabetes
Insulin resistance is the hallmarker of Type 2 diabetes and accumulating evidence show that inflammation plays a key role in obesity associated insulin resistance. Recently, Cell published the latest finding in Prof. Li Pingping's lab about inflammatory factor Galectin-3 (Gal3),Which is mainly secreted by macrophages. Prof. Li's group showed that Gal3 can directly bind to the insulin receptor and impair insulin signaling pathway in hepatocyte, adipocyte, and myocyte, then lead to the insulin res...
2016-12-12
 A novel hypoxia-responsive siRNA delivery system for tumor-targeted therapy developed by Prof. Gao Zhonggao’s group
Most solid tumors contain a tumor-specific microenvironment that is characterized by low pO2 , also known as hypoxia. Owing to the rapid proliferation of cancer cells, the tumor quickly exhausts the nutrient and oxygen supplied from the vasculature, and becomes hypoxic. Targeting hypoxia is considered as the best validated yet not extensively exploited strategy in cancer therapy. Recently, a research article entitled "an effective tumor-targeting strategy utilizing hypoxia-sensitive siRNA delive...
2016-10-21
A novel hypoxia-responsive siRNA delivery system for tumor-targeted therapy developed by Prof. Gao Zhonggao’s group
Most solid tumors contain a tumor-specific microenvironment that is characterized by low pO2 , also known as hypoxia. Owing to the rapid proliferation of cancer cells, the tumor quickly exhausts the nutrient and oxygen supplied from the vasculature, and becomes hypoxic. Targeting hypoxia is considered as the best validated yet not extensively exploited strategy in cancer therapy. Recently, a research article entitled "an effective tumor-targeting strategy utilizing hypoxia-sensitive siRNA delive...
2016-10-21
 TRB3, a metabolic stresses sensor acts as a biologic link between diabetes and cancer
Type 2 diabetes is a serious and growing health problem worldwide. Clinical and epidemiologic studies have shown that diabetes carries an increased risk for different forms of cancer, but with undefined mechanisms. High insulin and IGF-1 in circulation have been considered to be the most potential biologic links between the two diseases. However, clinical trials show that targeting insulin/IGF-1 signal does not produce satisfactory efficacy against cancers. Prof. Zhuo-Wei Hu's group in State Key...
2015-08-22
TRB3, a metabolic stresses sensor acts as a biologic link between diabetes and cancer
Type 2 diabetes is a serious and growing health problem worldwide. Clinical and epidemiologic studies have shown that diabetes carries an increased risk for different forms of cancer, but with undefined mechanisms. High insulin and IGF-1 in circulation have been considered to be the most potential biologic links between the two diseases. However, clinical trials show that targeting insulin/IGF-1 signal does not produce satisfactory efficacy against cancers. Prof. Zhuo-Wei Hu's group in State Key...
2015-08-22
 A novel advancement on targeting delivery of anticancer agents in Prof. Gao Zhonggao’s group
Recently, Prof. Gao Zhonggao's group, in the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, have published an original research paper entitled "Hybrid polymeric micelles based on bioactive polypeptides as pH-responsive delivery systems against melanoma" on Biomaterials (the impact factor was 7.604 published in 2013, with the 5-year impact factor of 8.496), an top international journal in the field of biomaterials and pharmaceutics. Now, the article is available o...
2014-07-07
A novel advancement on targeting delivery of anticancer agents in Prof. Gao Zhonggao’s group
Recently, Prof. Gao Zhonggao's group, in the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, have published an original research paper entitled "Hybrid polymeric micelles based on bioactive polypeptides as pH-responsive delivery systems against melanoma" on Biomaterials (the impact factor was 7.604 published in 2013, with the 5-year impact factor of 8.496), an top international journal in the field of biomaterials and pharmaceutics. Now, the article is available o...
2014-07-07
 Professor Zhu Ping's group published paper on Molecular & Cellular Proteomics
On May 10, 2013, Professor Zhu's group of the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines published (online) the article: Cloning and characterization of the glycoside hydrolases that remove xylosyl group from 7-β-xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol and its analogues (doi:10.1074/mcp.M113.030619) on Molecular & Cellular Proteomics (MCP), an international top journal in the field of proteomics (http://www.mcponline.org/content/early/recent) (the impact factor was 7.398 publ...
2013-05-29
Professor Zhu Ping's group published paper on Molecular & Cellular Proteomics
On May 10, 2013, Professor Zhu's group of the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines published (online) the article: Cloning and characterization of the glycoside hydrolases that remove xylosyl group from 7-β-xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol and its analogues (doi:10.1074/mcp.M113.030619) on Molecular & Cellular Proteomics (MCP), an international top journal in the field of proteomics (http://www.mcponline.org/content/early/recent) (the impact factor was 7.398 publ...
2013-05-29
 New advancement on siRNA drug delivery in Prof. Gao Zhonggao's group
Recently, a research article entitled "Anti-tumor effects in mice induced by survivin-targeted siRNA delivered through polysaccharide nanoparticles" in Prof. Gao Zhonggao' group in the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines has been published by the international authorized journal "Biomaterials" in the fields of biomaterials and pharmaceutics. Currently, this article is available online (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.03.047).
By inducing R...
2013-05-22
New advancement on siRNA drug delivery in Prof. Gao Zhonggao's group
Recently, a research article entitled "Anti-tumor effects in mice induced by survivin-targeted siRNA delivered through polysaccharide nanoparticles" in Prof. Gao Zhonggao' group in the State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines has been published by the international authorized journal "Biomaterials" in the fields of biomaterials and pharmaceutics. Currently, this article is available online (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.03.047).
By inducing R...
2013-05-22
 Dr. Zhuowei Hu group's work reveals the mechanism of IL17A suppressing autophagy
Dr. Zhuowei Hu and his group have recently published a paper entitled "Interlukin 17A inhibits autophagy through activation of PIK3CA to interrupt the GSK3B-mediated degradation of BCL2 in lung epithelial cells" in "Autophagy", an international reputation magazine. The research paper has been published online. In a previous work by this group, researchersreported that IL-17A promotes the development and progression of pulmonary fibrosis through TGFβ1-dependent and -independent mechanisms (Mi et ...
2013-02-28
Dr. Zhuowei Hu group's work reveals the mechanism of IL17A suppressing autophagy
Dr. Zhuowei Hu and his group have recently published a paper entitled "Interlukin 17A inhibits autophagy through activation of PIK3CA to interrupt the GSK3B-mediated degradation of BCL2 in lung epithelial cells" in "Autophagy", an international reputation magazine. The research paper has been published online. In a previous work by this group, researchersreported that IL-17A promotes the development and progression of pulmonary fibrosis through TGFβ1-dependent and -independent mechanisms (Mi et ...
2013-02-28
 TLR4 activity protects against hepatocellular tumorigenesis and progression
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a devastating consequence of chronic inflammatory liver diseases. The underlying molecular mechanisms for the relationships between HCC and chronic inflammatory are needed to be completely elucidated. TLR4 exhibit different sides with regard to the roles in the regulation of carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Researchers discovered that genetic or pharmacology blocking of TLR4 increases susceptibility to DEN-induced HCC development. TLR4 mutation results in s...
2013-01-24
TLR4 activity protects against hepatocellular tumorigenesis and progression
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a devastating consequence of chronic inflammatory liver diseases. The underlying molecular mechanisms for the relationships between HCC and chronic inflammatory are needed to be completely elucidated. TLR4 exhibit different sides with regard to the roles in the regulation of carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Researchers discovered that genetic or pharmacology blocking of TLR4 increases susceptibility to DEN-induced HCC development. TLR4 mutation results in s...
2013-01-24